It is important to understand that there is not only one blockchain, nor one single blockchain technology, but that blockchain is a concept, that refers to what is also called Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs). Ledger relates here to the traditional book of accounting where all the economic movements of an organizational entity (company, public administration, etc.) are recorded in chronological order. In this article, we will use Blockchain synonymously to DLT.
Although the blockchain technology was initially created to manage cryptocurrencies, it is nowadays not limited to economic transactions. Blockchain has for several years been used also to record “events” that occur and that we want to keep a record, and more recent blockchain technologies can also contain intelligence and work as autonomous agents, with smart contracts, that can serve as a base for new economic systems, which is referred to as token economies. Below we will look at some of these functionalities, as well as other important concepts and characteristics related to blockchain.
The basics function of Blockchain
Blockchain is in its basic version a software for registrations and transactions, that is installed on several computers in a network, which all run the same software. These distributed networks are called Peer to Peer (P2P) Networks, and the computers in the networks are called nodes. The blockchain software that runs on the computers, includes both the functionality of the blockchain, as well as a copy of the registry.
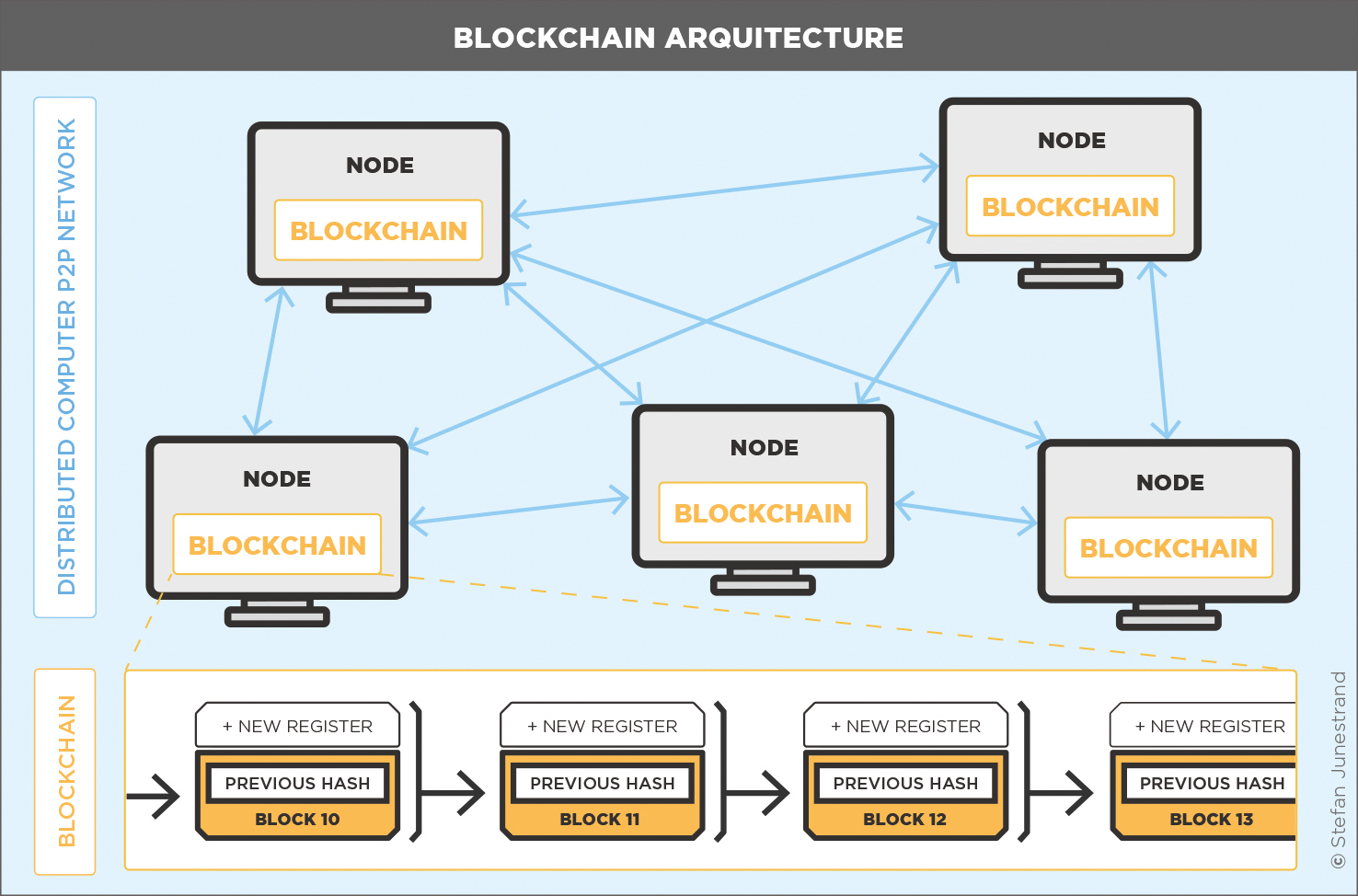
Model of the blockchain architecture with its principal elements.
When a new register is added to the blockchain, a new block of information is created, in which the new information, is combined with the information about the previous block, using complex mathematical algorithms.
The computer that first calculates the new block, sends it out to the other computers on the network for approval, and if approved, its added as a new block in the Blockchain and updated on all computers. So, this technology is called Blockchain, because it is actually a “chain of blocks”.
Smart contracts
The second generation of blockchain offers an additional functionality to the pure recording of data, and is called “smart contracts”. Smart contracts allow the blockchain to be programmed for automatic actions of any kind, triggered by any external action, based on simple conditional statements. Hence, users and actors can establish agreements based upon conditions of any kind, and when the conditions are fulfilled, the action is carried out as agreed.
Tokens
In blockchain systems, tokens are the representation of the different values and are the components used for the transactions within the system. Tokens can be of many types, but what they have in common is that they serve as an identifier for any kind of digital asset, which could be anything from monetary (as in cryptocurrencies) to physical assets (such as a piece of land) and even voting rights in a company, a private club, or a public election, etc. The tokens are technically a digital series of encrypted numbers (called a hash) which are stored by the users in their digital wallet and can only be used by accessing that wallet.
Blockchain wallet
The tokens on a blockchain are stored in digital wallets which each individual, organization, or even machine, uses to store their “keys” to access and use their tokens. This wallet can be viewed and used as an application on a pc or smartphone, or embedded in the software of an application.
DAPPS
A Dapp is a blockchain-enabled web application, although in blockchain the applications aren’t called Apps, but Dapps (decentralised applications), because they run on decentralised networks. The Dapps are built upon smart contracts and use “tokens” for the transactions within the application and can also use them to reward users that provide computing power to the network.
Different setups of blockchains
As mentioned above, blockchain is a flexible technology and can be applied in many different ways. When a blockchain is set-up and depending upon the needs of each application, there are two essential characteristics to consider:
- Public and private blockchains: A blockchain can be both public and private, as well as a hybrid between both. In a public blockchain (also called permission-less), anyone can join by setting up a copy of the database and participating, but in a private blockchain (also called permissioned), the owners of the application decide who may join the network and participate actively on it.
- Rights to read and write: Another aspect to define is who has the right to read the data, as well as who has the right to add data to the databases. For example, in a city that uses blockchain for their financial ledgers, the city administration should probably be the only one able to write new data, although any citizen should be able to read all the information.
What makes blockchain so revolutionary?
Blockchain is so disruptive and interesting due to 3 main characteristics and 1 revolutionary functionality.
The 3 main characteristics are:
- Transparent thanks to that anybody can see and read the data stored in a public blockchain, it makes it totally transparent.
- Immutable as nobody can change a previous block in the chain, it is immutable.
- Cybersecure due to the decentralized architecture, combined with the information stored in chains of blocks using complex cryptography, which makes it almost impossible to hack or attack.
The revolutionary functionality is the Token Economy, that makes it possible to build an economy not only based on a currency, but to use tokens, that can represent any value (currency, physical assets, services, rights, etc.) that can be given properties for conditional use using smart contracts.
